Diethylcarbamazine Citrate Tablet: What It Is and Why It’s Used

Introduction
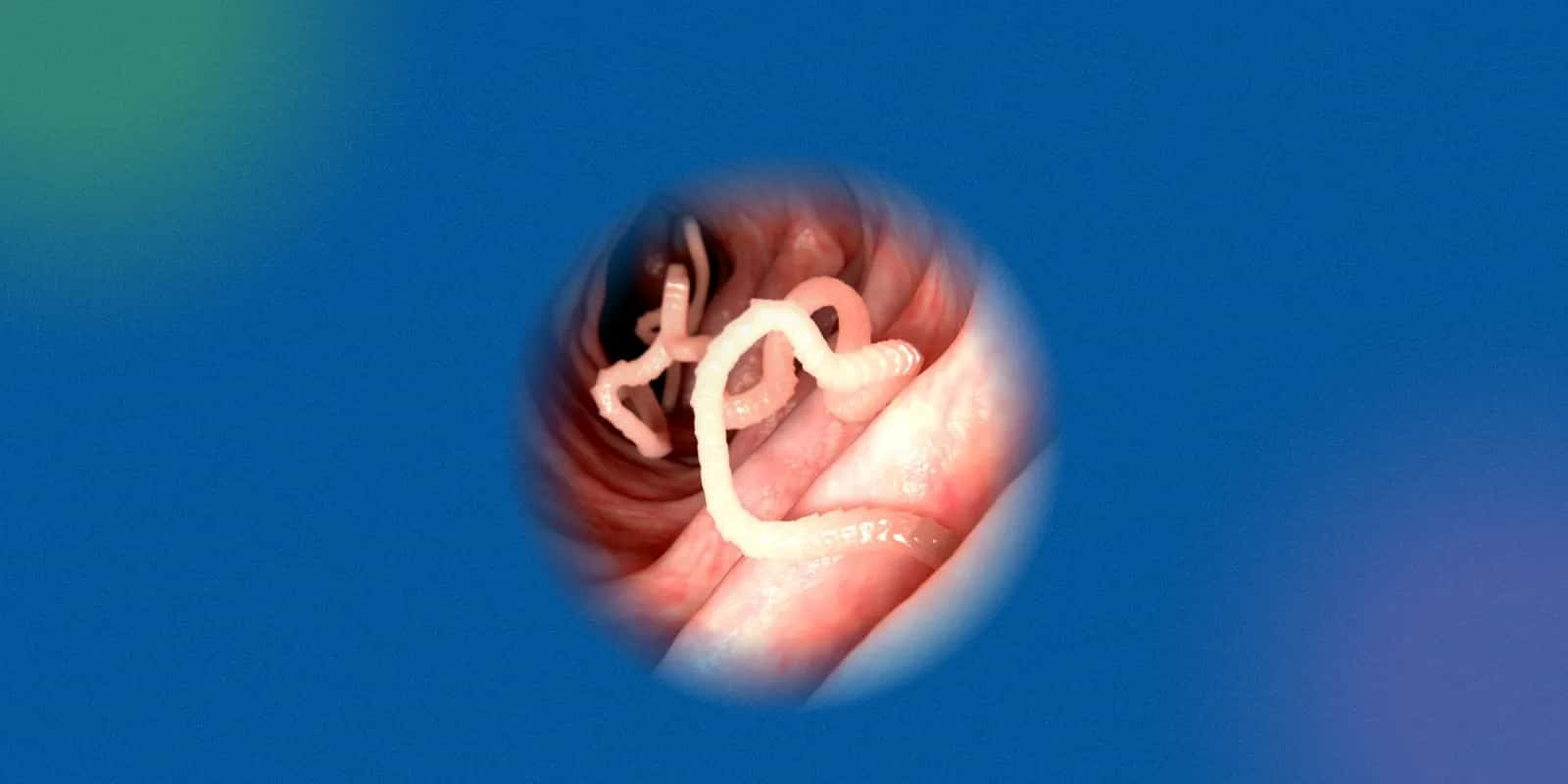
Filariasis is a mosquito-borne parasitic disease common in India and other tropical regions, often leading to chronic swelling, pain and disability. Diethylcarbamazine citrate (DEC), also known as Hetrazan, is a key medication used in its treatment and prevention.
This blog covers the drug’s mechanism, uses, dosage, side effects, and precautions, highlighting its role in managing filarial infections and public health.
What Is Diethylcarbamazine (DEC) and How Does It Work?
Diethylcarbamazine citrate (DEC) belongs to the class of antiparasitic drugs used to treat a range of worm infections. It works by altering the surface of the parasites, making them more vulnerable to the body’s immune response and leading to their destruction.
The medicine is widely prescribed in regions where filarial infections are common, including South Asia, Africa, and parts of South America. By targeting microfilariae (the larval stage of the worms), DEC helps eliminate infection early and reduces the risk of long-term complications.
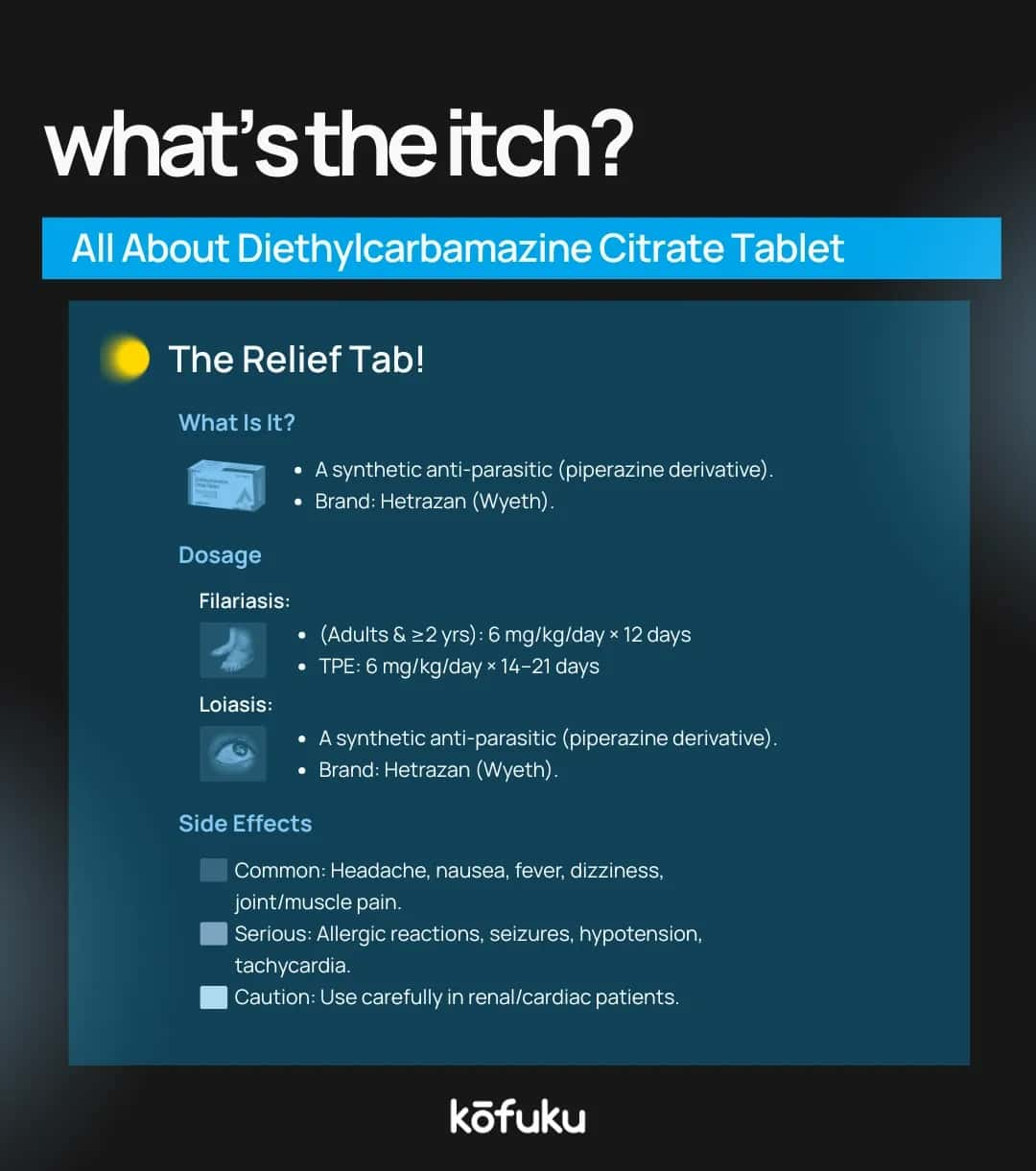
Available Strengths and Brand Names (Hetrazan 100 mg Tablet)
Diethylcarbamazine citrate 100 mg tablets are the most widely available form, sold under different brand names. In India, Hetrazan 100 mg tablet is the most used brand of tablets.
Hetrazan 100 Tablet Uses
The application of Hetrazan 100 tablet is in the treatment of Lymphatic filariasis and tropical pulmonary eosinophilia, and other parasitic diseases caused by thread-like worms. Hetrazan 100 mg tablet is highly effective and moderately priced.
Tab Hetrazan vs. Tablet Hetrazan
Patients often get confused between “tab Hetrazan” and “tablet Hetrazan.” Both terms refer to the same medicine. “Tab” is a short form used in prescriptions, while “tablet” is the common usage term.
Diethylcarbamazine Citrate 100 mg Uses
The main goal of prescribed diethylcarbamazine citrate tablets IP 100 mg is to get rid of microfilariae and alleviate such symptoms of parasite infestation as swelling, fever, or shortness of breath.
Therapeutic Uses of Diethylcarbamazine Tablets
The therapeutic scope of this medicine is broad especially in tropical medicine.
Medicine for Filariasis
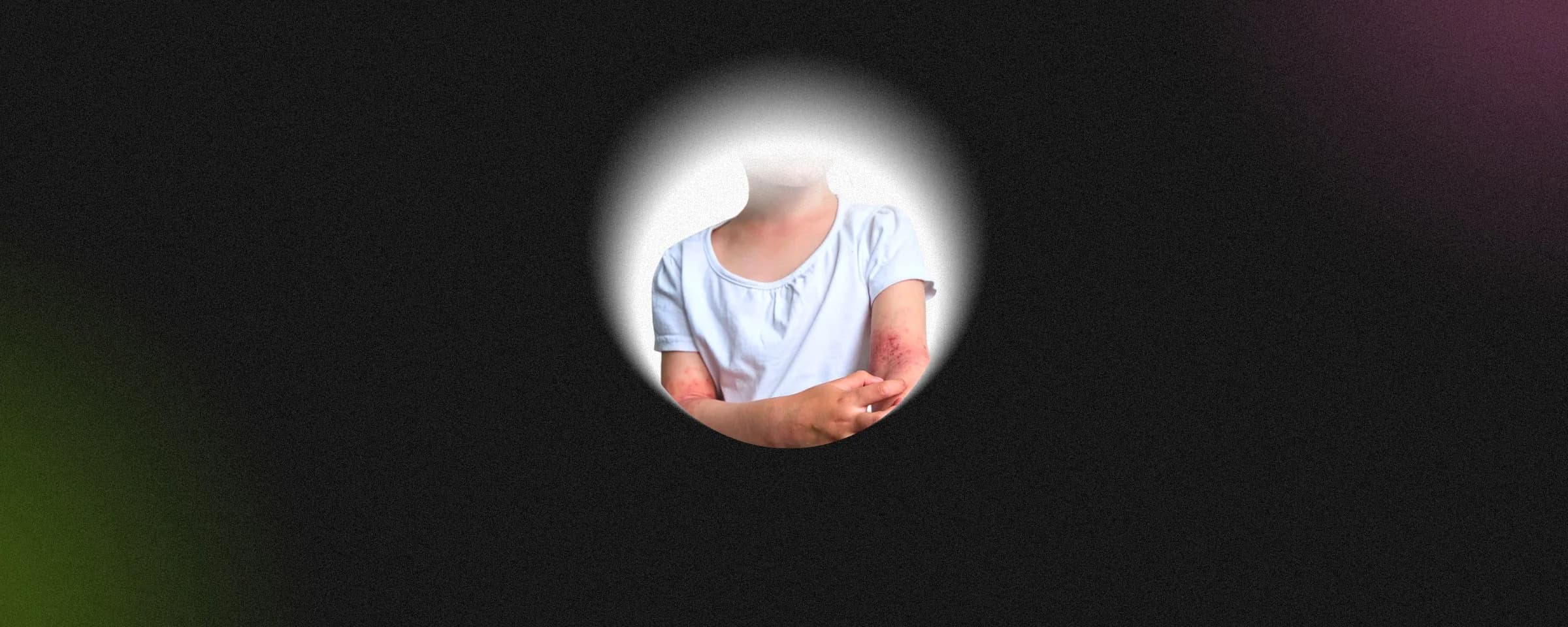
Diethylcarbamazine citrate tablets are commonly used to treat filariasis, a worm infection that causes lymphatic swelling. Regular use helps lower parasite load and prevent long-term complications.
Treatment of Tropical Eosinophilia & Related Diseases
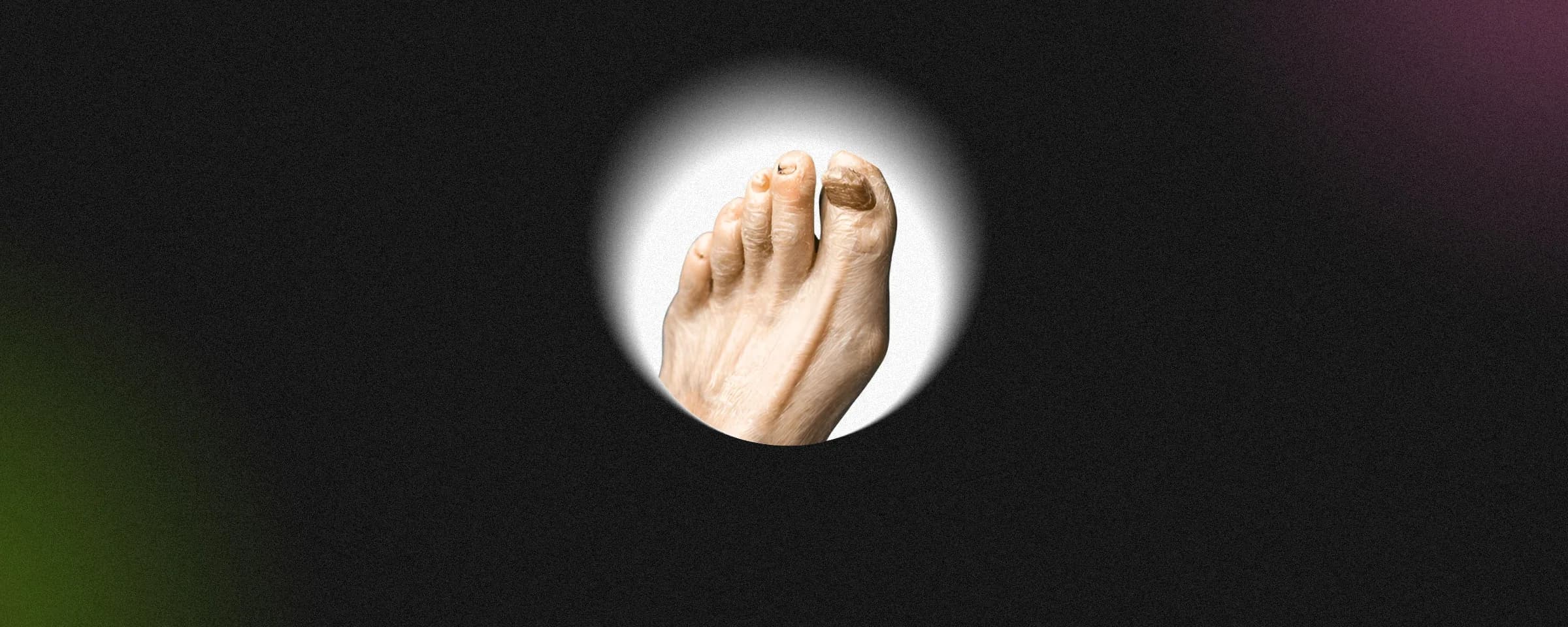
Physician use Hetrazan tablets in healing tropical eosinophilia, where the body produces an excess amount of white blood cells in response to worm infections. It can also be helpful in situations such as loiasis (worm of the eye) and a few other helminth diseases.
Dosage Guidelines for Diethylcarbamazine and Hetrazan
Dosage always depends on age, weight, severity of infection and the condition being treated.
Tablet Hetrazan 100 mg Standard Dosage
Adults are usually prescribed 100 mg Hetrazan two to three times daily, while children receive lower, weight-based doses. Dosage must follow medical advice to ensure effectiveness and minimise side effects.
Dissolve Tablet Use (if applicable)
Doctors may advise dissolving diethylcarbamazine citrate tablets in water for children or elderly patients who have difficulty swallowing, though this is usually done under medical supervision.
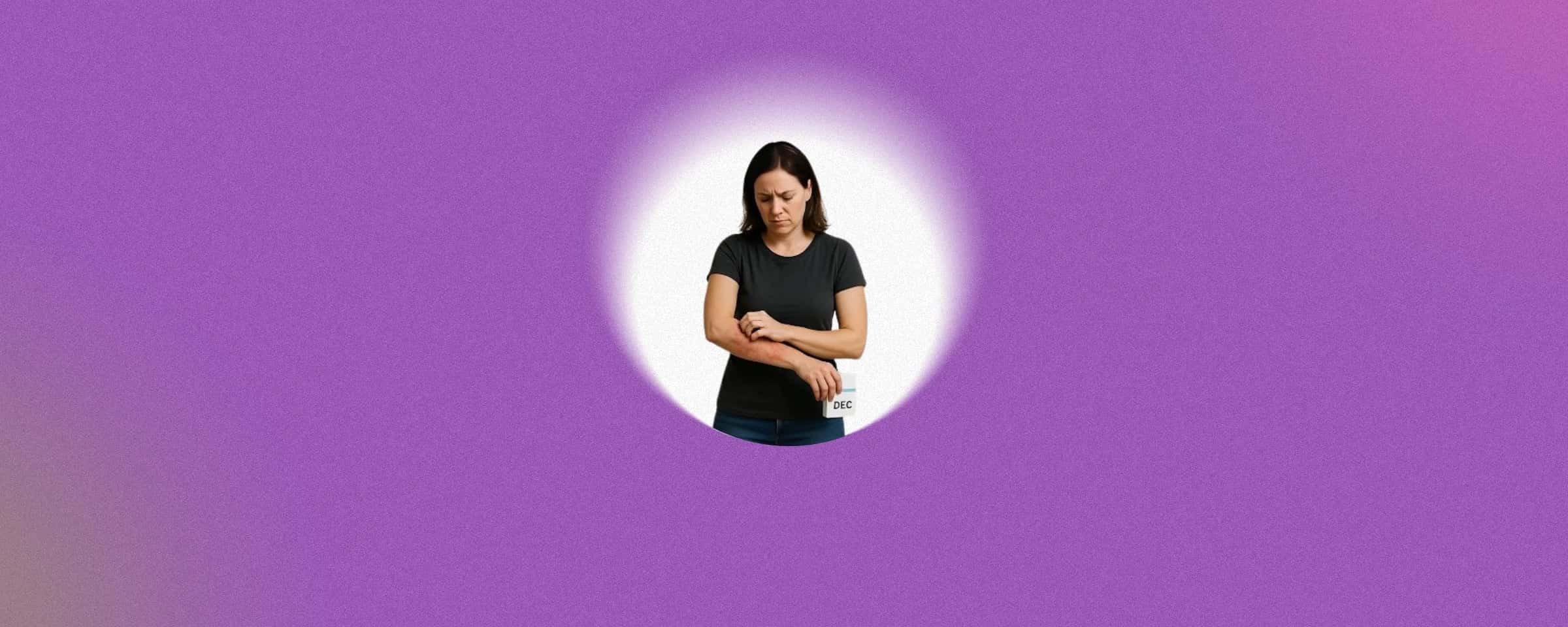
Side Effects and Risks of Hetrazan Tablet
Like all medicines, Hetrazan 100 mg may cause side effects. These can include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dizziness or headache
- Loss of appetite
- Allergic skin rashes
- Muscle or joint pain
Precautions Before Taking Diethylcarbamazine Citrate Tablets
Before starting tablet Hetrazan, patients should inform their doctor about:
- Any history of kidney or liver disease
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding status
- Allergies to antiparasitic drugs
- Other medicines they are currently taking
During long-term Hetrazan 100 use, doctors may monitor liver and kidney function with blood tests. Self-medication should be avoided to ensure safe and effective treatment.

Hetrazan vs. Other Anti-Filarial Medicines
There are other medicines for filariasis such as ivermectin and albendazole. However, diethylcarbamazine citrate tablets remain the gold standard in many regions.
- Ivermectin: More commonly used in Africa for onchocerciasis (river blindness).
- Albendazole: Effective against intestinal worms but less specific for filarial parasites.
- Hetrazan tablet: Specifically targets microfilariae and is considered highly effective in India and Southeast Asia.
FAQs
Q. What are Diethylcarbamazine citrate tablets?
A. Diethylcarbamazine citrate tablets treat parasitic infections like filariasis, loiasis, and tropical eosinophilia by targeting microfilariae and some adult worms, reducing related symptoms.
Q. What is the Hetrazan 100 mg tablet used for?
A. Hetrazan 100 mg (diethylcarbamazine citrate) is prescribed for filarial infections, reducing microfilariae, controlling inflammation, and relieving swelling, fever, and allergic symptoms.
Q. How does Hetrazan tablet work in filariasis treatment?
A. Hetrazan kills and weakens microfilariae, making them easier for the immune system to clear, reducing parasite load, symptoms, and filariasis complications.
Q. What is the dosage of Tab Hetrazan for adults?
A. The adult dosage of Hetrazan varies depending on the condition and severity. Typically, 6 mg/kg/day is given in divided doses for 12 days. Exact dosage must be prescribed by a physician after evaluating the patient’s weight, age, infection type, and medical history.
Q. Can tablet Hetrazan cure filariasis completely?
A. Hetrazan reduces parasite load and symptoms but may not fully cure chronic filariasis. Early treatment is more effective, while long-term cases may need repeated courses, supportive care, or surgery.
Q. What is the difference between Hetrazan 100 mg and other anti-filarial medicines?
A. Hetrazan (diethylcarbamazine citrate) targets filarial microfilariae and adult worms, with notable effectiveness against Wuchereria bancrofti and Loa loa. It is often combined with ivermectin or albendazole for broader treatment.
Q. What are the common side effects of Hetrazan tablet?
A. Common side effects include headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, and fatigue. Some patients experience allergic-type reactions due to dying microfilariae, such as fever, rash, itching, or swelling. These usually subside with supportive care or dose adjustment by doctors.
Q. How long should Diethylcarbamazine citrate tablets be taken?
A. The treatment duration depends on the infection type and the doctor’s prescription. Typically, Hetrazan is taken for 12 days, but courses may be repeated if required. Long-term or intermittent use may be advised for chronic infections under strict medical supervision.
Q. Can Hetrazan 100 tablets be used for children?
A. Yes, Hetrazan can be used for children, but dosage is strictly based on weight and the doctor’s recommendation. It is generally safe under supervision, though paediatric use requires caution to avoid side effects or complications due to developing immune systems.
Q. What should be avoided while taking the Hetrazan tablet?
A. Avoid alcohol, self-medication, or stopping Hetrazan abruptly. Use under medical supervision, especially with kidney, liver, or heart issues. Follow your doctor’s guidance closely.

Flavoxate Tablet: Everything You Need to Know About Urispas and Flavospas

Nitroglycerin Tablets and Injections: Everything You Should Know
Terbinafine Tablets: What They Are and How They Work

Understanding Levonorgestrel Oral Tablets: What They Are and How They Work

What is Sorbitol? Benefits, Tablet Uses, Side Effects and More