Olfactory Neuroblastoma - Causes, Symptoms, Treatment

Introduction
Imagine that you awake one particular morning with a strange sinus congestion, a slight decrease in your sense of smell, and a terrible, unexplained headache that won’t go away.
While these symptoms might seem benign at first, easily dismissed as a cold or allergies, however, for some these seemingly minor discomforts could be the sign of something more serious - olfactory neuroblastoma - a rare and often overlooked form of cancer.
In olfactory neuroblastoma, a tumour forms in the cells responsible for the sense of smell, located in the upper part of the nasal cavity. While this is quite rare, it can come with symptoms that are like that of common ailments, making diagnosis a challenge and a time-consuming process. As we progress in this blog, we’ll go through the causes, symptoms, treatment options and the issues that patients face when they suffer from this uncommon condition.
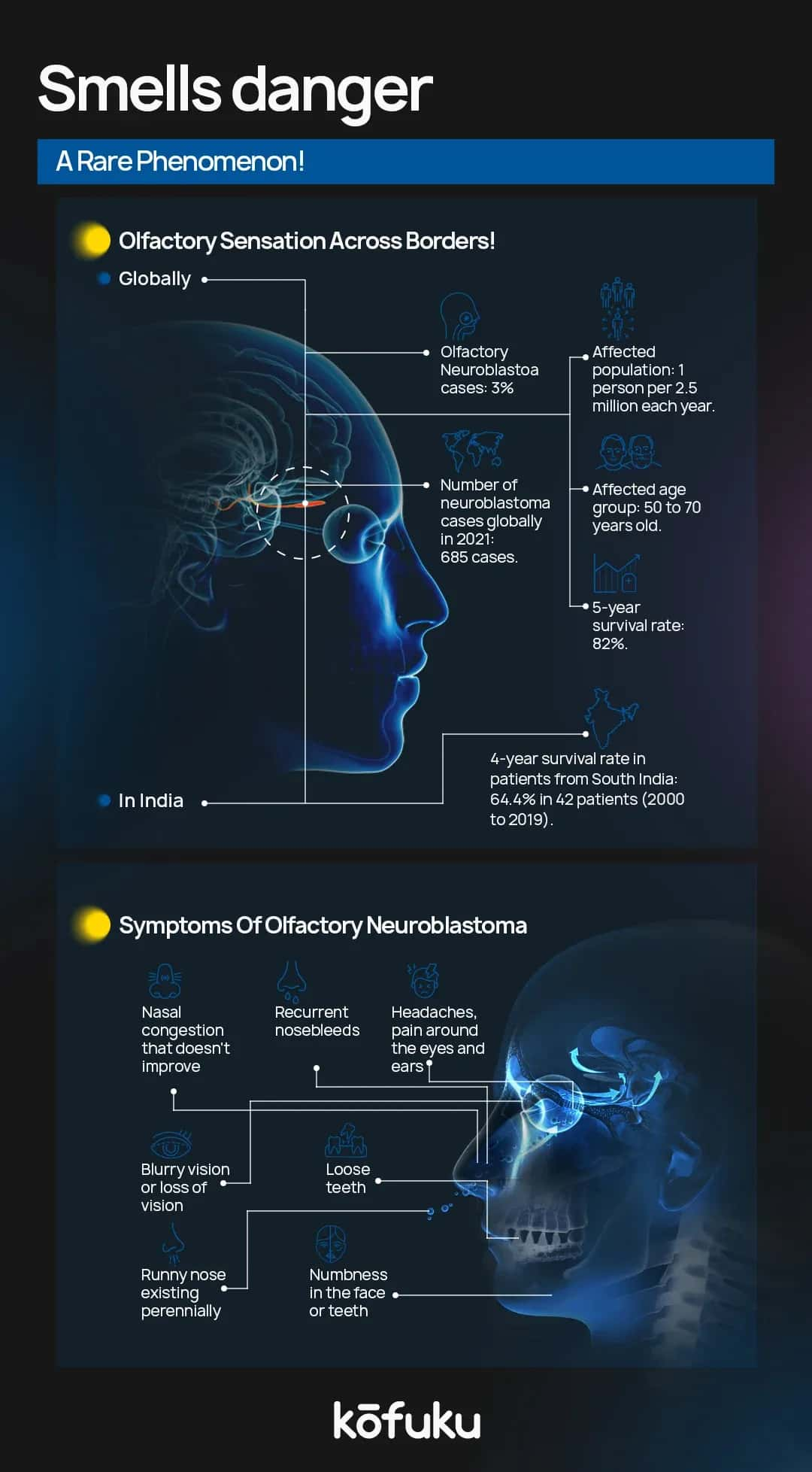
This cancer begins specifically in the nerves that impact the sense of smell. It is also known as esthesioneuroblastoma. This cancer often occurs on the roof of the nasal cavity. It involves the cribriform plate, which is a bone that lies between the eyes and located deep in the skull. When this cancer hits you it does so without any warning. The tumour grows in the nasal cavity, which is loaded with nerves and other tissues which are responsible for the sense of smell. This tumour starts in the nasal cavity and can grow into the nearby eyes and brain. Olfactory neuroblastoma can also spread to other body parts, like the neck, bones and lungs. A rare malignant tumour, it originates in the upper part of the nasal cavity, especially in the olfactory nerves which deal with the sense of smell.
How common is olfactory neuroblastoma?
This cancer isn’t exactly common - it makes up only 3% of nasal cavity tumour cases. Olfactory neuroblastoma impacts only about 1 person per 2.5 million people per year. Olfactory neuroblastoma can form at any age, yet it is mostly seen in people aged between 50 and 70 years.
Causes
Experts are still scratching their head when it comes to the exact cause of olfactory neuroblastoma also known as esthesioneuroblastoma. Usually, cancer occurs when cancer cells get changes in their DNA. A cell’s DNA contains the instructions which instruct the cell wrt to what to do. The changes tell the cells to make many more cells quickly. The changes give the cells the ability to carry on living when healthy cells would naturally die. This results in too many cells. THe cells might come together to form a mass known as a tumour. The tumour can grow to invade and destroy healthy body tissue. In time, cells can break away and spread to other body parts.
Symptoms of esthesioneuroblastoma
The symptoms of this cancer include :
-
Loss of sense of smell.
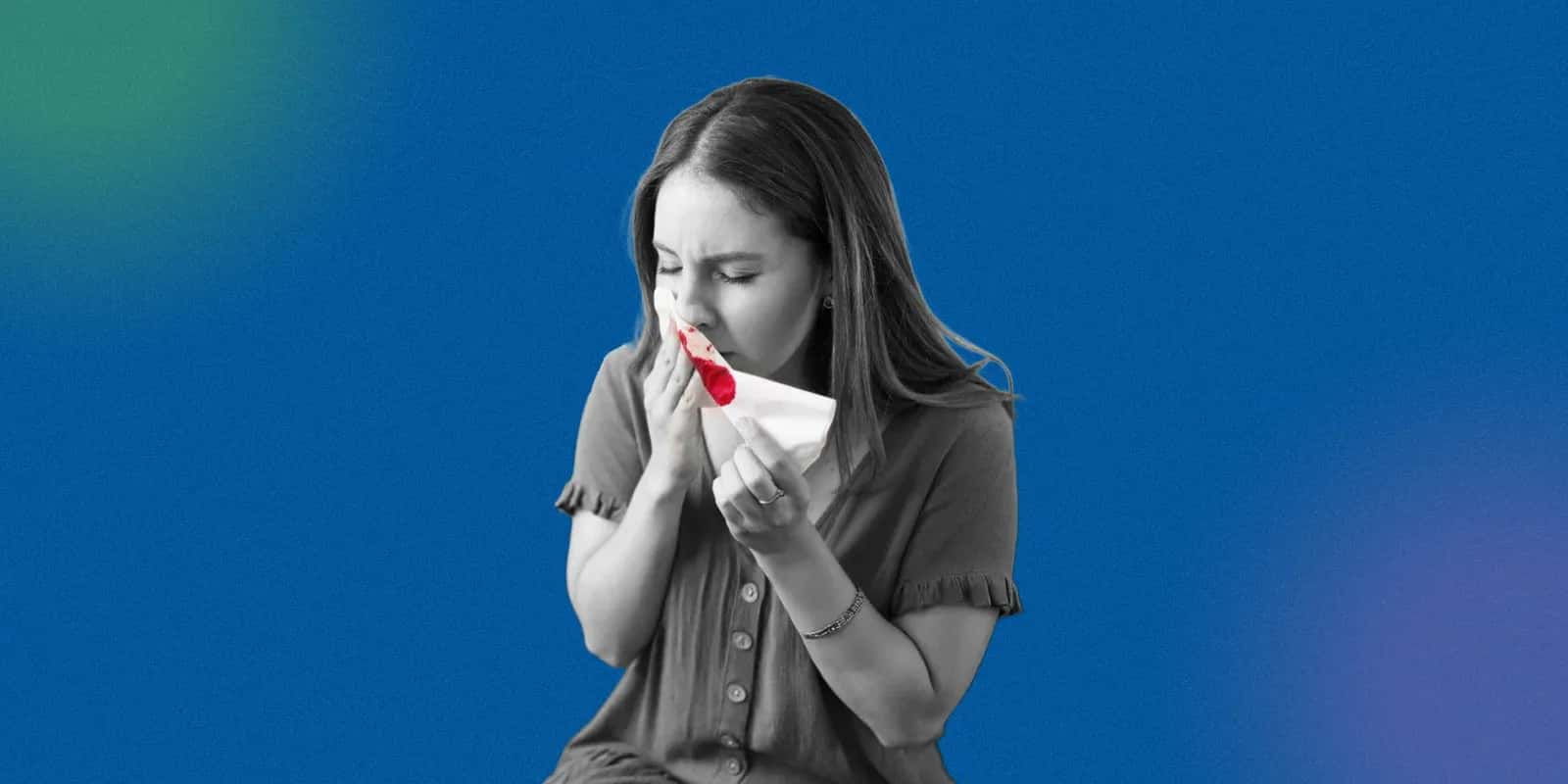
-
Frequent nosebleeds.
-
Issues with breathing through the nose.
-
As the cancer grows, it may cause eye pain, ear pain, loss of vision and headaches.
Complications of esthesioneuroblastoma
Complications of this kind of cancer include :
-
Cancer that grows into nearby organs and tissues. Esthesioneuroblastoma might grow and get into the sinuses, brain and eyes.
-
Spread of the cancer, also known as metastasis. Esthesioneuroblastoma can spread to other body parts like the bone marrow, liver, lymph nodes, bones and skin.

How is olfactory neuroblastoma diagnosed?
Doctors might diagnose this cancer by doing a bunch of imaging tests, and if required, a biopsy. Imaging tests might include :
-
Computed tomography (CT) scan
-
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan
-
Nasal endoscopy
-
Positron emission tomography (PET) scan
What are the stages of esthesioneuroblastoma?
Doctors depend on cancer staging systems to come up with treatment plans and a prognosis. The stages for this cancer are :
Stage A - Cancerous cells develop into a tumour in the nasal cavity.
Stage B - The tumour spreads straight from the nasal cavity to the nasal sinuses.
Stage C - The tumour spreads straight from the nasal cavity and sinuses towards the eyes or brain.
Stage D - Tests exhibit signs that cancer tumours have spread to other body parts, like the lymph nodes in the neck, lungs or bone marrow.
What are the treatments for esthesioneuroblastoma or olfactory neuroblastoma?
Healthcare providers usually do surgery to get rid of cancerous tumours. They might perform a :
-
Endoscopic surgery
-
Craniofacial surgery
-
Craniotomy
Other treatments are
-
Radiation therapy to eliminate any cancerous cells that remain post surgery.
-
Chemotherapy to treat esthesioneuroblastoma if tumours can’t be safely removed through surgery.
What is the recovery period for surgery to fix esthesioneuroblastoma or olfactory neuroblastoma?
Recovery time depends on the kind of surgery you have, having said that people stay in the hospital for around two to five days before convalescing at home. It might be one or two months before they receive radiation therapy.
What are the treatment side effects?
Surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy have different side effects :
-
Surgery side effects include pain, reaction to anesthesia and nasal fitness.
-
Common chemotherapy and radiation side effects are fatigue, vomiting, nausea and diarrhoea.
What are the treatment complications?
Once you get surgery for esthesioneuroblastoma, there might be some complications. Surgical complications might include :
-
A little too much bleeding.
-
Permanent loss of smell. There is a close connection between your sense of smell and sense of taste so you might end up losing that too.
-
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak.
-
Drainage in the nose that might feel dry and crusty.
What is the outlook/prognosis for esthesioneuroblastoma in adults?
Your prognosis (outlook) depends on the provider’s estimate of how a disease will impact you post treatment. Each person is different and prognosis might depend on a number of factors like :
-
Location of the tumour in the body.
-
If the cancer has spread to other body parts.
-
How much of the tumour was removed during surgery.
-
Results of lab work that exhibit tumour cell features.
Prognosis for esthesioneuroblastoma for children?
Like adults, the prognosis for this depends on the specific situation for children, with factors like tumour location, particular tumour cell features, whether this tumour has spread and how much of this tumour was successfully removed during surgery.
Survival rate for esthesioneuroblastoma or olfactory neuroblastoma
Healthcare providers postulate survival rates by looking at the experiences of people who have this condition. In this case, around 50% to 90% of people that have olfactory neuroblastoma were alive five years post diagnosis.
Is esthesioneuroblastoma fatal?
Cancer of the nose? This could be fatal. Esthesioneuroblastoma could spread to the lungs or other body parts. It can return post treatment and develop in other areas. Metastatic or recurrent esthesioneuroblastoma which slips away undetected could be life-threatening. Which is why regular check-ups are important so your provider could do imaging as well as other tests and grab cancer early on.
Conclusion
Esthesioneuroblastoma or olfactory neuroblastoma is an uncommon cancer which develops in the nose. Impacting nerves and tissues, it ruins your sense of smell. It develops over time. Sometimes, people think that its symptoms, namely nosebleeds, losing your sense of smell or nosebleeds aren’t serious enough to discuss with a healthcare professional. While a nosebleed is a nosebleed, however if a nosebleed is constant, your stuffy nose never clears up and you think your sense of smell has long gone, talk to a doctor. Get treatment and be cancer free.
FAQs
What is esthesioneuroblastoma (olfactory neuroblastoma)?
Esthesioneuroblastoma, also known as olfactory neuroblastoma, is a rare cancer that arises in the upper part of the nasal cavity, near the olfactory nerve, which is responsible for the sense of smell. It typically begins in the olfactory epithelium and can spread locally to nearby tissues or distant areas.
What are the common symptoms of olfactory neuroblastoma?
The symptoms of olfactory neuroblastoma can be subtle and often resemble other, more common conditions. Common signs include:
- A persistent nasal blockage or congestion
- Decreased sense of smell (anosmia)
- Frequent nosebleeds (epistaxis)
- Headaches
- Facial pain or swelling
- Loss of vision (in more advanced cases)
How is esthesioneuroblastoma diagnosed?
Diagnosis of esthesioneuroblastoma typically involves a combination of physical exams, imaging tests like CT scans or MRIs, and a biopsy of the tumor. An experienced doctor may also use endoscopic techniques to examine the nasal passages and identify the tumor. Early detection is key for effective treatment.
What treatment options are available for olfactory neuroblastoma?
Treatment for olfactory neuroblastoma depends on the tumor's size, location, and stage. Options include:
- Surgical removal of the tumor
- Radiation therapy to shrink or destroy cancer cells
- Chemotherapy, especially for more advanced or metastatic cases A multidisciplinary approach involving oncologists, surgeons, and radiation specialists is typically necessary.
What is the prognosis for patients with esthesioneuroblastoma?
The prognosis for esthesioneuroblastoma depends on the stage at which its diagnosed and the extent of spread. In early-stage cases, the survival rate is relatively high, especially if the tumor is completely removed. However, if the cancer has spread to other areas, treatment may be more complex, and the prognosis can be more guarded.