Home
Blogs
Wellness Corner
What is Hypothyroidism? Understanding Underactive Thyroid and Its Impact on Health
What is Hypothyroidism? Understanding Underactive Thyroid and Its Impact on Health

Introduction
Also known as an underactive thyroid, hypothyroidism is a common condition affecting millions of people around the world. Here, the thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough hormones. These hormones, primarily thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), regulate metabolism, energy production, and several key body functions.
When these hormone levels drop, multiple body functions slow down, leading to fatigue, weight gain, and other health problems.
Causes range from autoimmune diseases like Hashimoto’s to iodine deficiency, thyroid surgery, radiation therapy, and certain medications. While hypothyroidism is typically a lifelong condition, it can be managed effectively with proper treatment, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring.
Hypothyroidism Treatment Options: How to Manage Underactive Thyroid Effectively
The ideal treatment for hypothyroidism is to normalise thyroid hormone levels, manage symptoms, and prevent further health-related complications.
Levothyroxine Medication for Hypothyroidism: Dosage, Benefits, and Side Effects
Levothyroxine is the most common treatment for hypothyroidism as it is a synthetic version of thyroxine (T4) and simulates the thyroid hormone. The benefits include:
- Normalising thyroid hormone levels
- Increasing metabolism and energy levels
- Decreasing symptoms of fatigue, hair loss, and weight gain

Levothyroxine can have some side effects that can be due to an incorrect dose. The side effects include:
- Rapid heart rate or palpitations
- Nervousness or irritability
- Unexplained weight fluctuations
How to Find the Right Dosage of Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy
The dosage depends on:
- Age and weight
- Severity of hypothyroidism
- Heart disease
- Pregnancy
Your doctor will recommend blood tests (TSH and free T4) followed by repeat testing 6-8 weeks after starting treatment so that they can adjust your dosage accordingly. Once a patient's levothyroxine dose is stable, blood tests may be done every six to 12 months.
Lifestyle and Dietary Tips That Help Support Thyroid Health
Medication can help improve your thyroid function in the short-term, but you also need to make changes to your lifestyle and nutrition for sustainable, long-term results. Here’s what you can do:
- Eat iodine-rich foods like seaweed, dairy, and fish as suggested by your doctor or nutritionist, but in moderation.
- Ensure you have enough selenium intake through foods like Brazil nuts, tuna, or sunflower seeds.
- Avoid soy or cruciferous vegetables if your iodine intake is already low.
- Manage your stress and establish a healthy exercise routine.
- Be consistent with your medication.
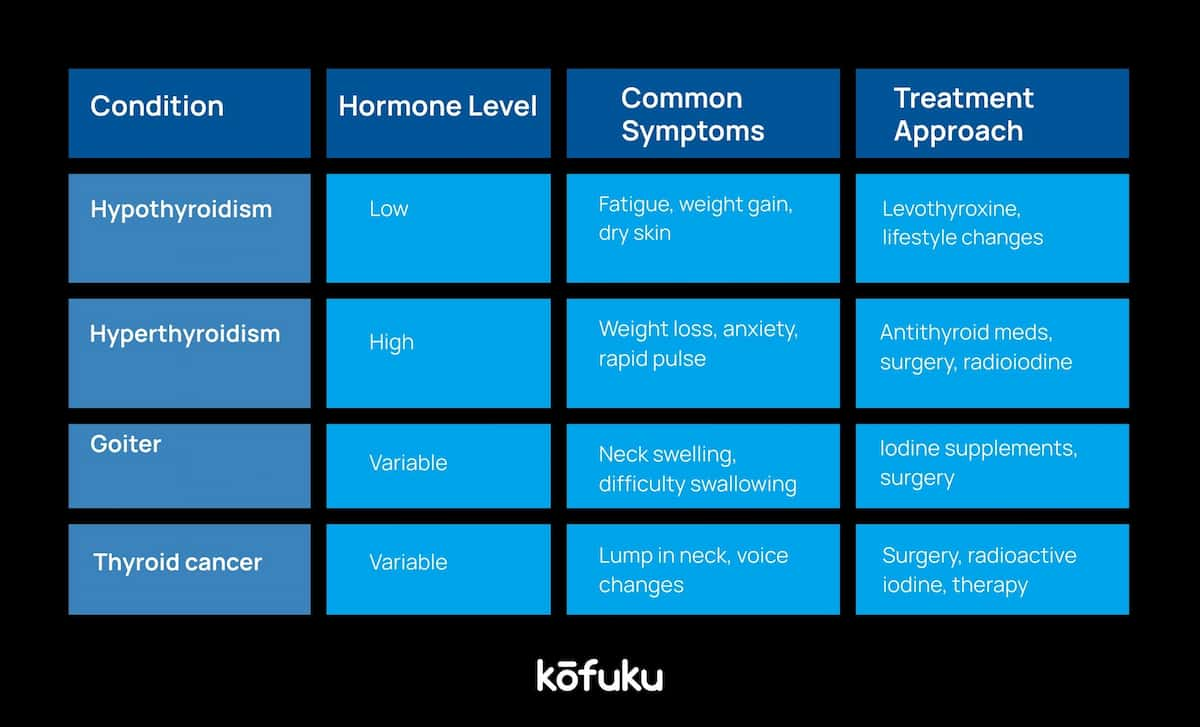
Understanding Thyroid Disease Beyond Hypothyroidism
Having thyroid doesn’t always mean that you have low iodine levels; it’s an umbrella term. Here is a list of common thyroid diseases:
- Hyperthyroidism: An overactive thyroid gland that produces too much hormone.
- Thyroid nodules: You can have lumps in your thyroid, but generally they are benign.
- Goitre: Enlarged Thyroid, usually due to iodine deficiency.
- Thyroid cancer: Requires treatment right away.

Common Thyroid Diseases and Their Differences
How to Check Your Thyroid at Home: Simple Steps and Tools
A blood test is the only method that can detect your thyroid function, but you can look for the early warning signs and perform a neck check yourself:
- Stand in front of a mirror, take a sip of water, and tilt your head back.
- As you swallow, observe whether your neck bulges or seems swollen.
- If you have any lumps in your neck, see a doctor.
At-Home Tests and When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
Home thyroid test kits measure TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone). To get a blood sample, follow the instructions by pricking your finger and then mailing the sample to a lab. Once you get the results, talk to your doctor.
You should also see a doctor if you have unexplained fatigue or other signs of concern, such as rapid weight change, thinning hair, or swelling in the neck.
Effects of Thyroidectomy on Women's Health: Impact on Menstrual Cycles and Periods
A thyroidectomy (surgical removal of the thyroid) is performed for thyroid cancer, large goitres, or extremely high hyperthyroidism.
Why Thyroidectomy Can Affect Periods and Hormonal Balance
Removing the thyroid will disrupt hormonal balance and alter:
- Timing of menstrual cycles
- Ovulation and fertility
- Severity of PMS symptoms
What to Expect After Thyroidectomy: Monitoring and Managing Symptoms
- Lifelong Levothyroxine therapy
- Blood tests to ensure proper hormone replacement
- Monitoring symptoms of low thyroid, including fatigue, changes in mood, and dry skin
Conclusion
Hypothyroidism is a chronic disease. However, people with this condition can still live normal and healthy lives, with proper diagnosis, treatment, and education. Once your hypothyroidism is diagnosed correctly and you’re on the appropriate dose of levothyroxine and have regular check-ins with your doctor, you’ll be able to manage your condition properly.
Staying educated and proactive will help you maintain good thyroid health, understand the risks, and avoid complications that may affect your general well-being.

FAQs
Q. What is the best hypothyroidism treatment today?
A. Levothyroxine is the most common and effective treatment for hypothyroidism, but your doctor must decide the dosage.
Q. How can I check my thyroid at home?
A. Do a self-check for swelling in the neck and note symptoms like fatigue or unexplained weight change. If you notice anything unusual or sudden changes, consult your doctor.
Q. What are the first signs and symptoms of thyroid disease?
A. Tiredness, sudden weight changes, hair loss, and skin dryness are some of the early symptoms to look out for.
Q. How long does hypothyroidism treatment take to show results?
A. Improvements may be seen in 2–4 weeks, but it is important to note that there is no cure. Proper treatment, lifestyle changes, and regular checkups can help you manage it.
Q. Does thyroidectomy affect periods and the menstrual cycle?
A. Yes, it can alter hormone balance, leading to irregular periods.
Q. Can hypothyroidism be cured naturally without medication?
A. Hypothyroidism cannot be cured, and most cases require lifelong hormone therapy. But diet and lifestyle help you manage the condition.
Q. What foods should be avoided if you have hypothyroidism?
A. Limit excessive soy, highly processed foods, and large amounts of raw cruciferous vegetables.
Q. Is levothyroxine safe for long-term use?
A. Yes, when taken as prescribed and monitored regularly.
Q. How often should thyroid levels be checked during treatment?
A. Initially, every 6–8 weeks, then every 6–12 months once stable.

10 Signs of Hypothyroidism That You Should Be Worried Of

7 Myths About Thyroid - This Is What You Should Know

Ten Signs of Hyperthyroidism That You Should Be Wary Of


