Home
Blogs
Lifestyle Diseases
Blood Sugar Level Chart Based on Age: Understanding Diabetes Normal Range and Related Values
Blood Sugar Level Chart Based on Age: Understanding Diabetes Normal Range and Related Values

Introduction
In India, blood sugar check is commonly a part of regular checkups, even if one does not have diabetes. As the number of patients with diabetes increases both in urban and rural areas, it is crucial to explore how age, diet, and lifestyle affect sugar levels in the blood.
The normal range chart for diabetes can help you better understand your health, whether you are a teenager, a working professional, or an elderly citizen.
This blog explores age-wise blood sugar levels, key medical tests, and related values such as HbA1c normal level range, rheumatoid factor normal value, PPBS blood sugar normal range, and insulin normal value, giving you a practical reference point for better management.
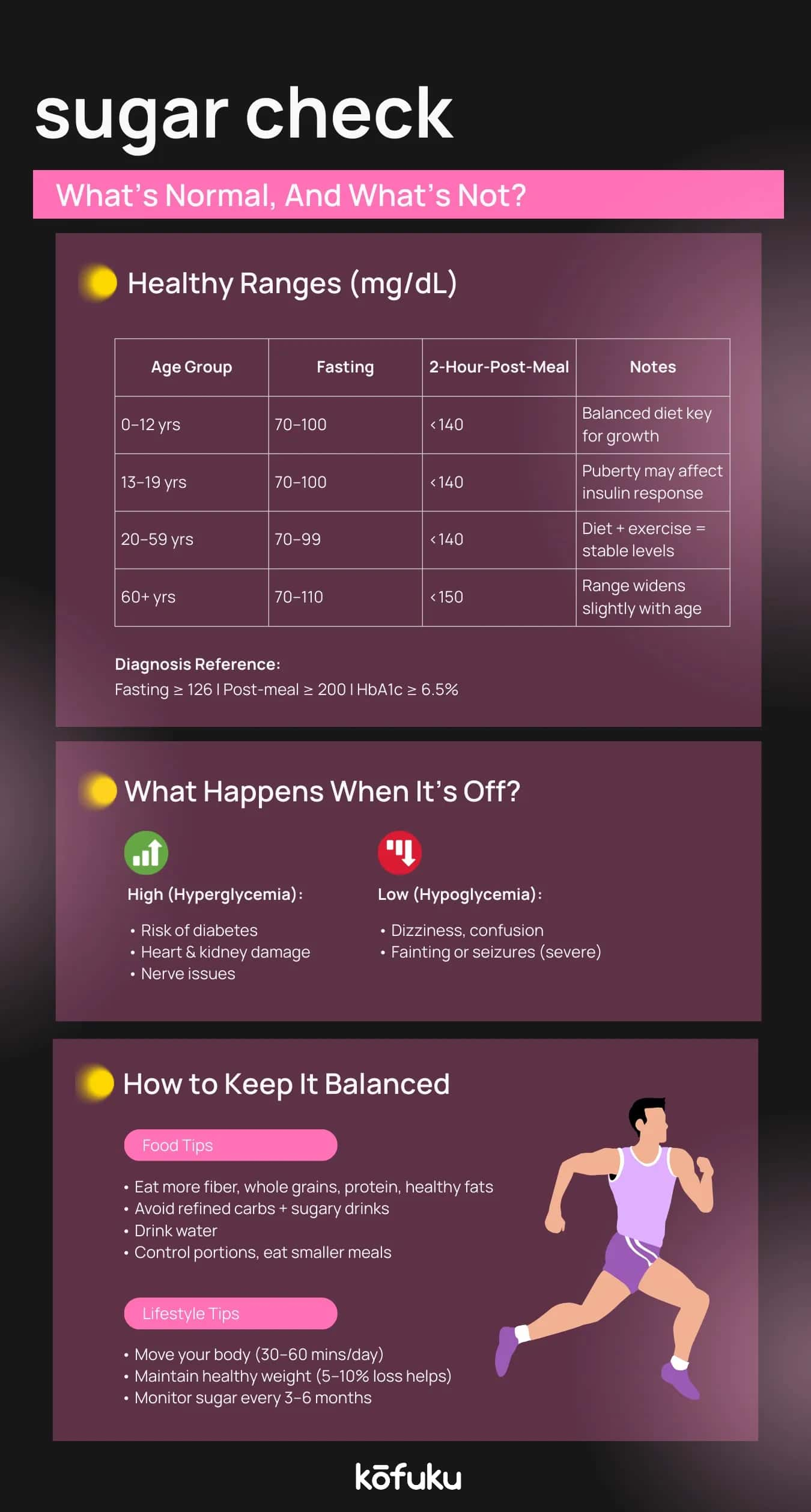
What is a Diabetes Normal Range Chart? Explanation of Blood Sugar Levels by Age
A diabetes normal range chart is a table that identifies the normal levels of fasting, postprandial, and average blood sugar in people of varying age groups. Glucose, also known as blood sugar, is the primary source of energy for the body. Unusually high or low levels could be an indication of diabetes and other health issues.
Typically:
- For children, fasting blood sugar should remain slightly lower than that of adults.
- For adults, levels are more stable, with clear distinctions between fasting (before meals) and postprandial (after meals).
- For older adults, a slightly relaxed target may be acceptable due to changes in metabolism.
Understanding HbA1c: Normal Level Range and Its Importance
HbA1c normal level range indicates your long-term average blood sugar over the last two or three months. Compared to a single blood test, it provides an overall view of long-term glucose control.
- Normal: Below 5.7%
- Prediabetes: 5.7% to 6.4%
- Diabetes: 6.5% and above
Medical practitioners typically use HbA1c rates to determine whether there is a need to adjust medication or make lifestyle changes. A patient who has borderline high fasting sugar may be termed as having diabetes when they have a higher HbA1c level.
What is the Rheumatoid Factor Normal Value and Its Relation to Blood Sugar?
The normal rheumatoid factor is less than 20 IU/mL. Although this test is primarily used to identify autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, it may also have an indirect connection to blood sugar levels.
The presence of high rheumatoid factor may lead to difficulty using insulin in the body due to chronic inflammation. Such an association denotes why some of the patients with autoimmune problems have higher risks of developing insulin resistance and rising glucose levels.

PPBS Blood Sugar Normal Range: What Does Postprandial Blood Sugar Indicate?
Postprandial blood sugar (PPBS) measures glucose levels two hours after a meal. The PPBS blood sugar normal range helps doctors understand how effectively your body processes food and regulates insulin.
- Normal: Less than 140 mg/dL
- Prediabetes: 140–199 mg/dL
- Diabetes: 200 mg/dL or higher
PPBS Test Normal Range: How to Interpret Your Results
The PPBS test normal range differs, depending on the diet, the age of the person, and existing conditions. In adults under 60 years of age, a level below 140 mg/dL is considered safe. Higher levels can be acceptable in the case of seniors.
The results of PPBS are interpreted in conjunction with fasting blood sugar and HbA1c levels to gain a deeper understanding. A chronically elevated PPBS is typically indicative of impaired carbohydrate metabolism and may require dietary adjustments or medical intervention.
Insulin Normal Value: What It Means for Your Blood Sugar Control
Insulin within normal limits in the fasting state is generally between 2 and 20 units/mL. Insulin is the hormone that moves glucose from the blood into your cells, allowing the body to use its energy.
Low amounts are abnormal because they can signal the presence of type 1 diabetes, in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin. Conversely, high fasting insulin levels are an indicator of insulin resistance, which is commonly a precursor to type 2 diabetes. Maintaining healthy insulin levels is essential for blood sugar control.
FBS and PPBS Normal Range: Differences and What They Mean for Your Health
The FBS and PPBS normal ranges are often considered simultaneously to have an overall view of glucose regulation.
-
FBS (Fasting Blood Sugar): Below 100 mg/dL (normal), 100-125 mg/dL (prediabetes), 126 mg/dL and above (diabetes).
-
PPBS (Postprandial Blood Sugar): Below 140 mg/dL (normal), 140-199 mg/dL (prediabetes), 200 mg/dL or higher (diabetes).

Age-Wise Blood Sugar Levels: Charts and Guidelines for Different Age Groups
Blood sugar targets can vary with age. Here is a simplified guideline:
- Children (6–12 years): Fasting 80-120 mg/dL, PPBS below 140 mg/dL
- Adolescents (13–19 years): Fasting 70-130 mg/dL, PPBS below 140 mg/dL
- Adults (20–59 years): Fasting 70-100 mg/dL, PPBS below 140 mg/dL
- Older adults (60+ years): Fasting 80-140 mg/dL, PPBS below 160 mg/dL
Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Levels Across Ages
Several factors can influence whether blood sugar falls within or outside the diabetes normal range chart:
-
Diet: High intake of refined sugars and carbohydrates leads to spikes.
-
Physical activity: Regular exercise improves insulin sensitivity.
-
Ageing: As metabolism slows down, the risk of elevated glucose levels increases.
-
Hormones: Changes during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause can disrupt balance.
-
Medications: Steroids, for example, may increase blood sugar levels.
-
Stress and illness: Both can temporarily push glucose above normal values
How to Monitor and Maintain Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring blood sugar is crucial for both individuals with diabetes and those without. Common methods include finger-prick testing, continuous glucose monitoring devices, and periodic HbA1c checks.
To maintain healthy levels:
- Follow a balanced diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, and proteins.
- Engage in regular physical activity.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Get adequate sleep and manage stress.
- Follow medical advice if prescribed medications or insulin.
Common Symptoms of High and Low Blood Sugar to Watch For
Recognising symptoms helps prevent emergencies.
-
High blood sugar (hyperglycaemia): Excessive thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision, fatigue.
-
Low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia): Sweating, dizziness, confusion, rapid heartbeat, shaking.
FAQs
Q. What is the normal blood sugar level chart by age?
A. The normal blood sugar level chart by age outlines recommended fasting and postprandial ranges for children, adults, and seniors, helping monitor and control diabetes and prevent complications effectively.
Q. What is the normal range for HbA1c levels?
A. The HbA1c normal level range is typically below 5.7%. A level between 5.7–6.4% is indicative of prediabetes, and 6.5% or higher indicates diabetes. It is important to not self-diagnose and consult a doctor to know what changes you need to make.
Q. What does a positive rheumatoid factor mean?
A. A positive rheumatoid factor normal value test may indicate autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. However, it can sometimes be present in healthy individuals or in association with other diseases, so further clinical evaluation is necessary.
Q. What is the normal range for the PPBS blood sugar test?
A. The PPBS blood sugar normal range is usually less than 140 mg/dL in healthy individuals. Levels between 140–199 mg/dL suggest prediabetes, while 200 mg/dL or above indicates diabetes.
Q. How is the PPBS test different from the FBS test?
A. The PPBS test normal range checks blood sugar two hours after meals, while FBS (fasting blood sugar) measures levels after fasting overnight. Together, FBS and PPBS normal range confirm diabetes control.
Q. What are the normal insulin levels in the blood?
A. The normal insulin value in fasting adults is usually 2–20 µIU/mL. Levels may vary depending on health, diet, and testing conditions, which can indicate pancreatic function and insulin sensitivity.
Q. How often should blood sugar levels be tested?
A. Testing frequency depends on age, diabetes status, and treatment. Diabetics may test daily, while non-diabetics or prediabetics should follow the doctor’s advice, with periodic FBS and PPBS checks.
Q. What factors can affect blood sugar levels across different ages?
A. Diet, physical activity, stress, medications, hormonal changes, illnesses, and aging significantly affect blood sugar levels. Understanding age-related variations helps interpret the diabetes normal range chart accurately for better management.
Q. What symptoms indicate high or low blood sugar levels?
A. High blood sugar may cause frequent urination, excessive thirst, and fatigue, while low blood sugar triggers symptoms such as sweating, shakiness, dizziness, confusion, or fainting, requiring immediate attention.

12 Unusual Symptoms of Diabetes

7 Diabetes-Friendly Fruits for Diabetic Patients

Black Rice for Diabetes: A Nutritional Weapon Against High Blood Sugar
IBS and Diabetes: The Unholy Alliance

Beyond the Bump: Why Diabetes in Pregnant Women Demands Your Attention Now

Mushrooms: Nature’s Secret Ally in Diabetes Control and Management

Diet and lifestyle: key to diabetes prevention


