Comprehensive Guide to Cefpodoxime Syrup and Tablets: Dosage, Benefits, and Uses

Introduction
Cefpodoxime is a prescription antibiotic available in various forms, including Cefpodoxime syrup, Cefpodoxime Proxetil tablets, and combination drugs like Cefpodoxime CV, which contains additional ingredients such as Potassium Clavulanate. This is an effective drug that doctors use to treat a range of bacterial infections and is widely used due to its effectiveness, broad spectrum of action, and a low side-effect profile if used as prescribed.
Whether your prescription states Cefpodoxime 200 mg, Cefpodoxime 500 mg, or some other dosing strength, it's important to have a thorough understanding of how to take it, what it treats, and what to watch for.
This article will help you understand the types of Cefpodoxime, dosage guides for various ages, and other information that you need to know to use it safely.
What is Cefpodoxime Proxetil? Understanding the Syrup, Tablets, and Combination Forms
Cefpodoxime Proxetil is an oral, third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic available in many forms. Once you ingest it, the Proxetil is converted to Cefpodoxime, which is the "active" drug that kills bacteria.
Key Types: Cefpodoxime Syrup, Cefpodoxime Proxetil Tablet, Cefpodoxime CV
Cefpodoxime syrup: A liquid suspension, most commonly prescribed for children or for a patient who cannot swallow a tablet. It usually comes with a measuring cup or spoon for dosing purposes.
Cefpodoxime Proxetil tablet: A solid oral tablet meant for adults and older children who don’t have any trouble swallowing pills.
Cefpodoxime CV: A combination medicine containing cefpodoxime Proxetil and Potassium Clavulanate. The Clavulanate is used to block bacterial enzymes (Beta-Lactamases), which can cause bacteria to be antibiotic-resistant.
Dosage Details: Cefpodoxime 200 mg, 500 mg, Per Kg and Tablet IP 200 mg
The dosage is heavily dependent on the type of infection, age, weight, and kidney function of the patient. Your doctor will customise your prescription accordingly.
Age-wise Dosing: How to Use Cefpodoxime for Children, Adults, and the Elderly
- Children:
The dosage of this medicine is often calculated per kg of body weight. The typical range is 5–10 mg/kg/day in two divided doses. For example, a child weighing 20 kg who is prescribed 10 mg/kg/day would need 200 mg total daily and would need to take two doses of 100 mg each.
- Adults:
The typical adult dosing of Cefpodoxime is 200 mg every 12 hours for respiratory tract infections or as prescribed, with different dosages for specific symptoms.
- Elderly people:
Dosages are often the same as adults; however, it is important to check renal function and ensure that patients don’t need any additional dose adjustments.
Combination Medicines: Cefpodoxime Proxetil and Potassium Clavulanate: Uses and Benefits
Doctors generally use combination therapy with Cefpodoxime Proxetil and Potassium Clavulanate if the infection is caused by bacteria that produce enzymes with the ability to deactivate the effects of Cefpodoxime. Potassium Clavulanate inhibits these enzymes, allowing Cefpodoxime to take effect.
How Does Cefpodoxime Work? Mechanism, Action, and Expected Results
Cefpodoxime works by interfering with bacterial cell wall synthesis, without which the bacteria cannot survive. It is bactericidal (kills the bacteria), rather than just inhibiting their growth.
Most patients will start to feel better within 48-72 hours of starting therapy. However, you must still take the entire course of the prescribed medication, as it's vital to help prevent relapse as well as mitigate and avoid antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
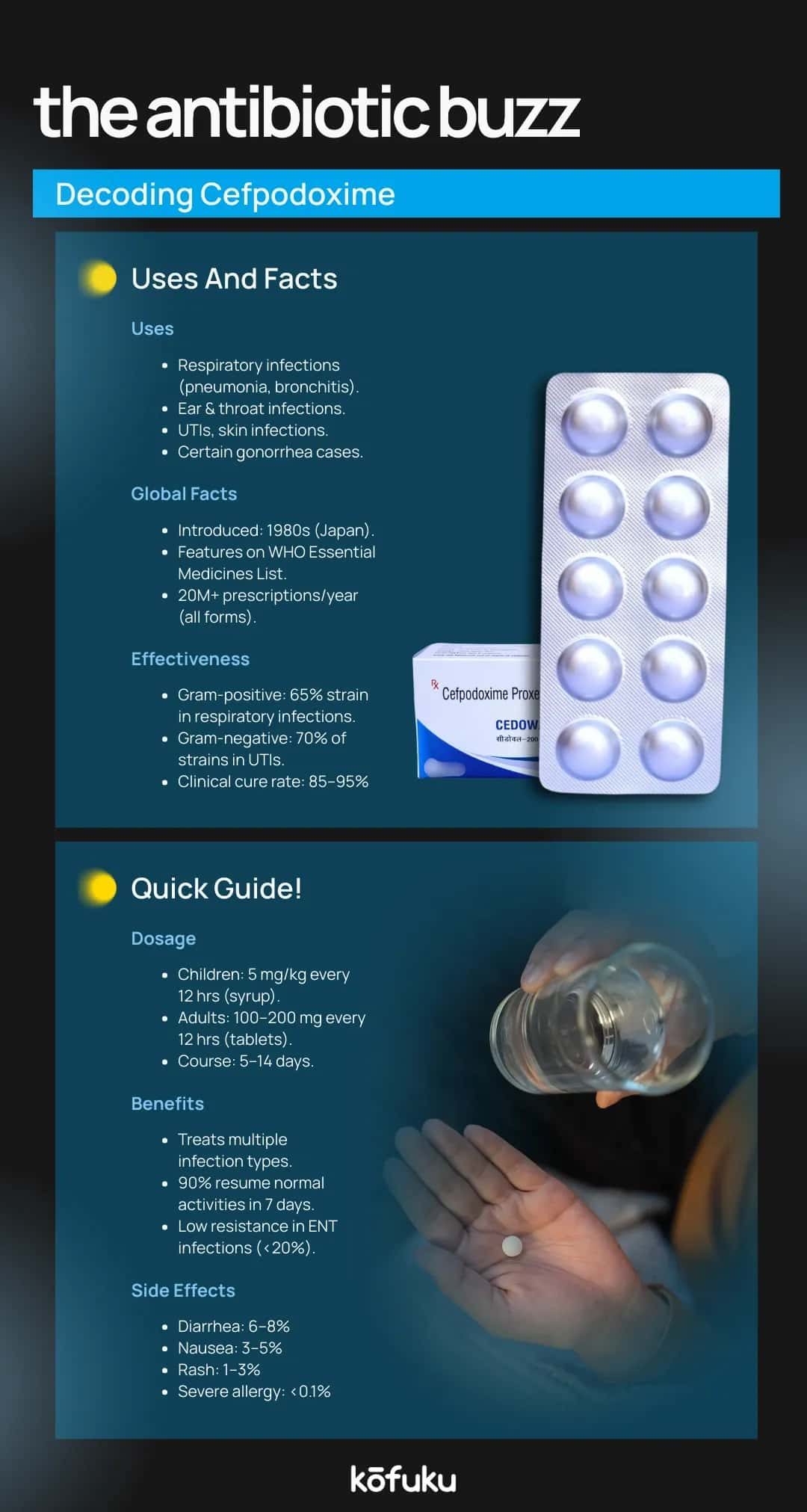
Common Indications: When Your Doctor Prescribes Cefpodoxime (Throat, UTI, Sinus Infections)
Doctors prescribe Cefpodoxime for:
- Throat infections (e.g., strep throat and tonsillitis)
- Urinary tract infections (UTI)
- Sinus infections (sinusitis)
- Ear infections (otitis media)
- Bronchitis and pneumonia
- Skin infections
Step-by-Step: How to Take Cefpodoxime Syrup and Tablets Safely
Here is a quick guide on how to administer the syrup and tablets:
Syrup: Shake well before use to mix it thoroughly.
Tablets: Take tablets whole with water and do not crush unless directed by your doctor.
Dose: Follow the instructions for dose and frequency as advised by the doctor, or label, if needed.
With Food: Taking cefpodoxime with food can increase the rate of absorption.
Timing: Take doses at intervals, if possible, to maintain steady drug levels in your body, as recommended by your doctor.
Safe Use Guidelines: Storage, Missed Dose, and When to Consult a Doctor
Storing the medication correctly is crucial to maintaining its effectiveness. Here’s how you can do it:
Syrup: Should be stored as per the instructions mentioned on the label. Tablets: Store at room temperature; keep them away from moisture.
Missing a dose or two is common, especially when you are not feeling well. Here’s what to do if and when that happens:
-
Take it as soon as you remember, only if there’s enough time until the next dose
-
If it's almost time for your next scheduled dose, then skip the missed dose. Never double up.
Go to a doctor immediately if you develop rash eczema, severe diarrhoea, or any symptoms of allergic reaction, breathing issues, or unexplained persistent fever.
Side Effects, Warnings, and Drug Interactions for Cefpodoxime
Cefpodoxime is usually safe; however, there may still be some potential side effects. These include:
- Allergic reactions presenting as itching, skin rash, hives, swelling of the lips, throat, or tongue
- Severe diarrhoea, fever
- Vaginal itching, unusual discharge, or odour
Go to your doctor if you develop any of the above symptoms to ensure prompt treatment. You may also experience some mild side effects, such as diarrhea, headache, and nausea, which are not serious but should be reported to your doctor.
Important Precautions: Who Should Not Take Cefpodoxime?
Try to avoid or take caution with Cefpodoxime if you:
-
Are allergic to cephalosporins or penicillin.
-
Have severe kidney disease and cannot have your dose adjusted.
-
Are taking other medications that could interact with Cefpodoxime (e.g., antacids, diuretics, or probenecid).
Final Thoughts
The bottom line is that cefpodoxime syrup and cefpodoxime proxetil tablets are helpful in the treatment of various bacterial infections if taken as directed by a doctor. Knowing your prescription, how to take your Cefpodoxime, and when to contact your doctor will help ensure your treatment is safe and effective.
FAQs
Q. What is the proper cefpodoxime dosage per kg for children?
A. The dosage for children is usually 5–10 mg/kg/day, but your doctor will determine the exact amount based on the child’s age, weight, and type of infection.
Q. When to use cefpodoxime proxetil and potassium clavulanate tablets?
A. This combination is prescribed when the infection is suspected to be caused by beta-lactamase–producing bacteria that can resist regular cefpodoxime. The clavulanate component blocks this resistance.
Q. Can cefpodoxime syrup be used for all types of infections?
A. No. Cefpodoxime only works against bacterial infections. It is not effective for viral illnesses such as the flu or common cold.
Q. What is cefpodoxime CV 325/200?
A. Cefpodoxime CV is a combination drug. The numbers (325 or 200) refer to the strength in milligrams of cefpodoxime, sometimes combined with potassium clavulanate to improve effectiveness against antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Q. How does the cefpodoxime proxetil tablet IP 200 mg differ from other tablets?
A. “IP” refers to the Indian Pharmacopoeia, meaning the tablet meets specific Indian drug standards. The 200 mg strength is a common dose for adults, but it may vary by infection type.
Q. Are there known side effects of cefpodoxime 500?
A. Yes. Side effects can include nausea, diarrhoea, abdominal pain, headache, and rash. Contact your doctor immediately if severe symptoms develop.





