Understanding Cataracts: Causes, Symptoms, and Effects on Vision

Introduction
Did you ever notice a member of your family complaining about a lack of clarity in seeing or having halo effects on objects of light? Cataracts are a common cause of undiagnosed blindness in India, often mistaken for other vision problems.
Although it is such a widespread condition, not every person understands the early warning signs or the impact cataracts can have on lifestyle. Such ignorance usually causes a delay in the treatment, leading to deterioration in the quality of life.
This blog will help you understand more about the causes, signs, and symptoms of cataracts, their effects on vision, and how they can be managed through medical and natural means.
Physiology of Sight: How the Eye Works and How Cataracts Affect Vision
The human eye is much like a camera. Light enters the eye through the cornea, passes through the lens, and focuses on the retina, enabling the brain to interpret the images. This is what is known as the physiology of sight.
In a cataract, the lens that is usually clear becomes cloudy. The vagueness alters the penetration of light, causing the vision to be impaired. Patients generally refer to it as seeing through fogged glass. Although cataracts usually are age-related, other conditions, like trauma, diabetes, and lifestyle behaviour, e.g, smoking, can cause them.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Cataracts: What to Watch For
Prevention of extreme eyesight loss is possible at an early stage. Cataract's main signs and symptoms include:
- Blurry or cloudy vision resembling mist or haze.
- Difficulty seeing at night, often worsened by glare.
- Seeing halos around lights, especially noticeable while driving at night.
- Yellowing or fading of colours, making objects appear dull.
- Frequent changes in glasses prescription, as the condition alters refraction.
- Double vision in one eye, which may clear as the cataract matures.
Types of Vision Defects Related to Cataracts and Other Conditions
Cataracts do not form the only defects of vision, although they contribute to more than one. Common problems are:
- Myopia (short-sightedness): Difficulty seeing distant objects.
- Hyperopia (long-sightedness): Difficulty focusing on nearby objects.
- Astigmatism: Blurred vision due to uneven corneal curvature.
- Presbyopia: Age-related difficulty in focusing on nearby objects or work.
Cataract Lenses and Brown Colour Lenses: How Vision Correction Helps
Cataracts can best be treated through surgery. In the process, the affected lens is substituted with the use of an artificial intraocular lens (IOL), otherwise known as cataract lenses.
Other lenses, e.g., brown colour lenses, are used to minimise glare and block blue light to improve contrast sensitivity. They are particularly important for patients who report feeling discomfort in brightly illuminated conditions. The lens is decided based on medical counselling, lifestyle requirements, and budgetary feasibility.
Pictures of Cataracts: Recognising Eye Changes
While written descriptions help, visual identification is often more effective. Pictures of cataracts eye or a cataract eye pic typically show a whitish or cloudy appearance at the centre of the pupil. Photographs can create awareness, but self-diagnosing with them is unreliable and not advised.
The Eyes Have It: Common Questions and Answers About Cataracts
- Can cataracts be prevented? Not entirely, but delaying onset is possible with healthy habits.
- Are cataracts painful? No, but they gradually impair vision.
- Is surgery safe? Yes, modern cataract surgery has a high success rate with minimal downtime.
- Do cataracts recur after surgery? The replaced lens does not develop cataracts again, though a condition called posterior capsular opacification may occur.
How to Improve Eyesight Naturally: Tips and Lifestyle Adjustments
- Balanced diet rich in antioxidants: Leafy greens, carrots, and citrus fruits promote retinal health.
- Adequate hydration: Prevents eye dryness and strain.
- Quitting smoking: Even lighter smoking increases oxidative stress on the eyes.
- Wearing UV-protective glasses: Prevents sun damage to eye tissues.
- Eye exercises and proper rest: Reduce fatigue and maintain focus.
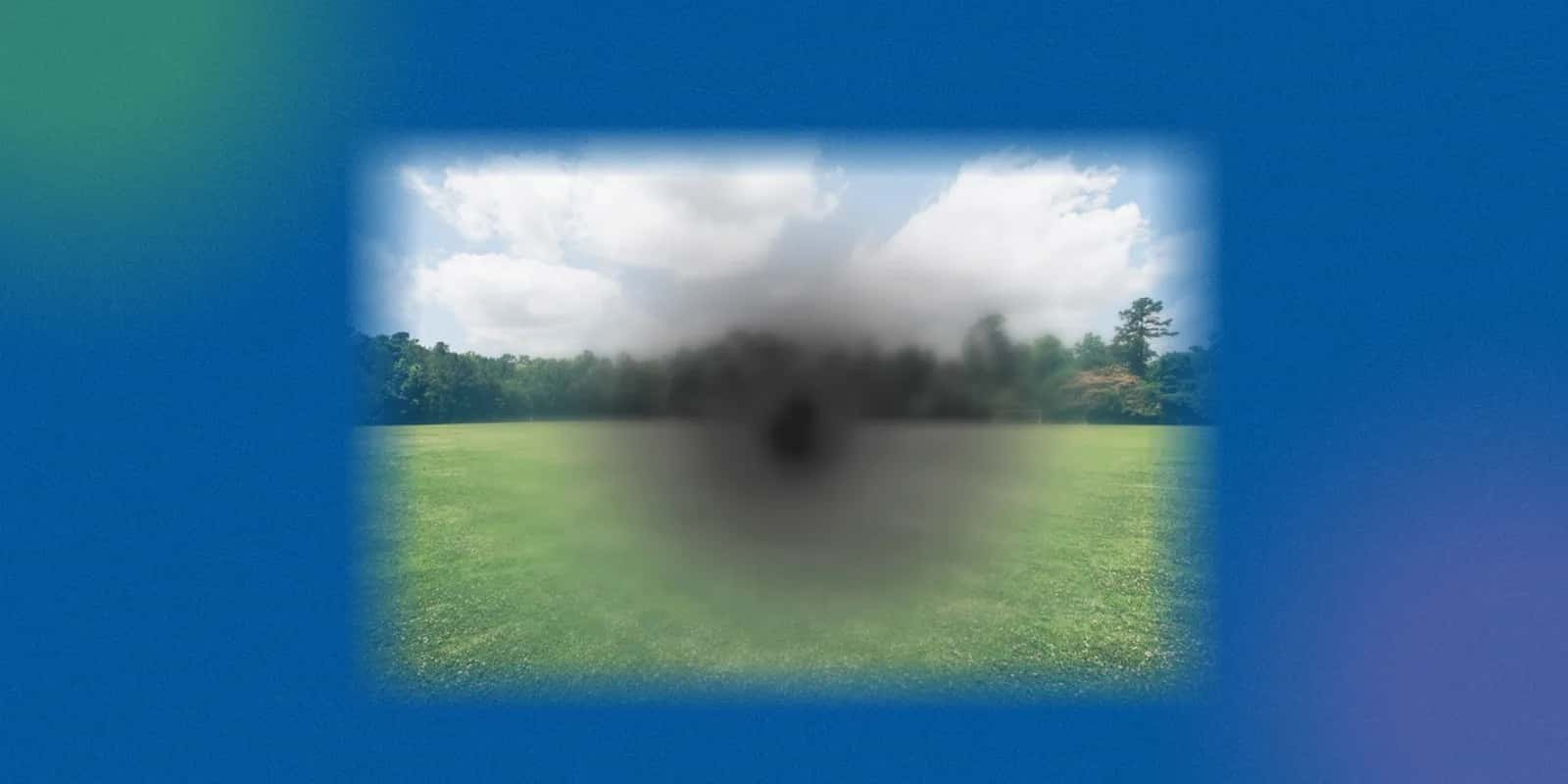

Managing Light Sensitivity and Disturbances: Tips for Better Vision
Cataract patients often report discomfort in bright light or difficulty reading when exposed to glare. Some tips to adjust for this include:
- Using anti-glare spectacles for outdoor use.
- Installing softer indoor lighting to reduce strain.
- Wearing brown colour lenses is recommended for glare management.
- Avoiding exposure to direct bright light during activities like studying.

FAQs
Q. What are the most common signs and symptoms of cataracts?
A. Cataracts often cause cloudy or blurred vision, difficulty seeing at night, fading colours, sensitivity to glare, frequent prescription changes, double vision in one eye, and seeing halos around lights.
Q. Can cataracts cause defects in vision?
A. Yes. Cataracts cause defects of vision by clouding the natural lens, leading to blurred or dim vision, poor contrast sensitivity, and problems with everyday activities like reading and driving.
Q. What is corneal opacity, and how does it differ from cataracts?
A. Corneal opacity clouds the cornea, the outer transparent surface of the eye. Cataracts, however, affect the internal lens, producing similar but distinctly located defects in vision.
Q. How do cataract lenses, including brown-coloured lenses, help improve vision?
A. Cataract lenses, especially advanced intraocular lenses, replace the cloudy lens after surgery. Brown-coloured lenses filter glare and blue light, enhancing contrast, reducing discomfort, and improving visual clarity post-treatment.
Q. Why do cataracts cause seeing halos around lights?
A. As cataracts cloud the lens, light scatters instead of focusing clearly. This scattering produces glare and circular rings, leading patients to report seeing halos around lights, especially at night.
Q. What is the physiology of sight, and how do cataracts affect it?
A. The physiology of sight involves light entering the eye, focusing on the retina, and forming images. Cataracts disrupt this process, scattering light, reducing clarity, and causing eyesight defects.
Q. Are there pictures of cataract eyes to help identify the condition?
A. Yes, pictures of cataract eyes often show a cloudy or whitish lens in the pupil. While helpful for awareness, they should not be relied upon for a diagnosis. Only a professional examination is a reliable way to confirm it.
Q. How can I improve my eyesight naturally if I have early cataracts?
A. While cataracts cannot be reversed naturally, healthy habits like antioxidant-rich diets, UV protection, quitting smoking, hydration, and regular eye check-ups help slow progress and support overall eye health.





