Home
Blogs
Lifestyle Diseases
Understanding Hyperthyroidism: Causes, Symptoms, and Importance of Treatment
Understanding Hyperthyroidism: Causes, Symptoms, and Importance of Treatment

Introduction
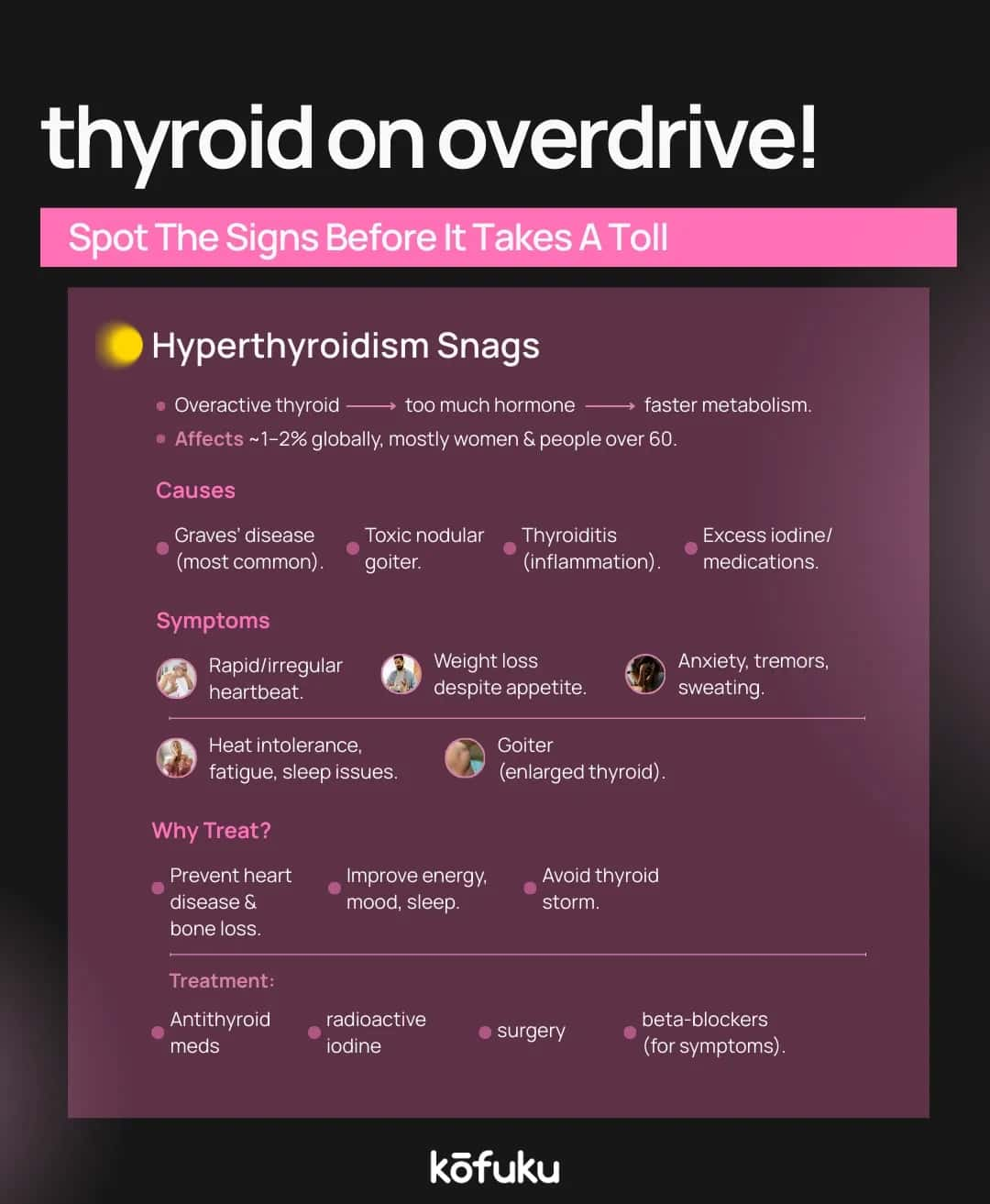
Have you ever heard of people suddenly losing weight despite maintaining good eating habits, or suddenly experiencing heart palpitations and being unable to sit still, despite seemingly nothing causing this? People often attribute these symptoms either to stress or weakness, but the problem in most instances is an overactive thyroid gland.
This condition, known as hyperthyroidism, can seriously affect health if left untreated. Recognising its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for early intervention and long-term well-being.
Hyperthyroidism Treatment Options: Medical and Lifestyle Approaches
Individualised treatment is greatly sought when an individual is tackling hyperthyroidism. It mainly depends on the age of the person and the strength of the symptoms, as well as the cause. The three main medical alternatives are:
- Antithyroid medications:
Drugs such as methimazole or propylthiouracil reduce hormone production. These are often the first line of treatment and may be continued for several months.
- Radioactive iodine therapy:
This method damages overactive thyroid cells, lowering hormone levels. It is a common choice in both India and Western countries.
- Surgery (thyroidectomy):
In cases of severe goitre or cancer suspicion, part or all of the thyroid may be removed. Patients often need lifelong thyroid hormone replacement afterwards.
Gentle exercise routines such as walking or low-impact aerobics can be good for individuals with hyperthyroidism as they support cardiovascular health without overstraining the body.
Foods to Avoid for Hyperthyroidism: Dietary Guidelines for Better Management
- Iodine-rich foods such as seaweed, kelp, and iodised salt may worsen the condition.
- Caffeinated drinks like tea, coffee, and energy drinks can intensify symptoms such as palpitations and anxiety.
- Highly processed foods contribute to inflammation and may aggravate weight fluctuations.
- Gluten-rich products (for those with autoimmune thyroid disease, like Graves’ disease) should be limited as they can trigger immune responses.

Nursing Diagnosis of Hyperthyroidism: Key Focus Areas
In clinical practice, a nursing diagnosis of hyperthyroidism helps guide patient care. Nurses typically focus on:
- Imbalanced nutrition due to increased metabolic demands.
- Disturbed sleep patterns caused by restlessness and anxiety.
- Activity intolerance as a result of muscle weakness or fatigue.
- Risk of cardiac complications, including tachycardia and hypertension.
- Altered body image due to weight loss, hair changes, or eye-related symptoms like exophthalmos (bulging eyes).
Hyperthyroidism Nursing Care Plan: Goals and Interventions
A nursing care plan for hyperthyroidism is well-developed to stabilise a patient and improve their quality of life. The standard objectives are to:
- Promoting adequate rest and sleep.
- Encouraging balanced, nutrient-dense meals.
- Monitoring vital signs such as pulse and blood pressure.
- Educating patients about medication compliance.
Nursing Interventions for Hyperthyroidism: Practical Management Strategies
Treatment of hyperthyroidism by nursing tends to deal with risks and symptom management:
- Ensuring a calm, low-stress environment.
- Advising small, frequent meals to counter weight loss.
- Encouraging hydration to manage heat intolerance.
- Teaching relaxation exercises.
- Observing for complications like thyroid storm, a life-threatening condition requiring urgent care.
Good nursing care not only solves physical needs; it also helps to instill confidence in patients so that they can handle their condition.
Role of Hyperthyroidism Specialists: When and Why to Consult
It is necessary to visit a specialist dealing with hyperthyroidism, i.e., an endocrinologist, as it promotes accurate diagnosis and consequent planning of the treatment plan. General practitioners may identify symptoms, and specialists will offer specific treatment based on a range of tests on hormone levels, ultrasound scans, and medical tests in specific cases.
Rapid, inexplicable weight loss, irregular heartbeat, profuse sweating, and nervousness are among the signs that require immediate medical consultation. Learning about the condition early will allow correct monitoring and prevent long-term complications such as heart disease or osteoporosis.

Hyperthyroidism Pictures and Images: Visual Guide to Recognising Symptoms
The pictures and images used to describe hyperthyroidism can depict indicators of the presence of the disease, such as protruding eyes, swollen thyroid glands (goitre), or loss of weight. Although such pictures can be beneficial to raise awareness of this disease, it is important to know that hyperthyroidism doesn’t present the same way in all individuals.
For instance, one may exhibit outward symptoms like tremor, whereas another may not reveal outwardly but inwardly signs, such as palpitations or mood disorder. So, remember a professional opinion cannot be substituted by the single use of the pictures.
Difference Between Hyperthyroidism and Thyrotoxicosis: Clarifying Terms
People often confuse hyperthyroidism with thyrotoxicosis, but they are not identical.
- Hyperthyroidism refers specifically to the overproduction of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland.
- Thyrotoxicosis describes the clinical state that results when excess thyroid hormones circulate in the body, regardless of the cause.
FAQs
Q. What are the most effective treatment options for hyperthyroidism?
A. The most effective hyperthyroidism treatment options include antithyroid medications, radioactive iodine therapy, and surgery. Lifestyle changes and monitored exercise also help control symptoms and maintain long-term health.
Q. Which foods should I avoid if I have hyperthyroidism?
A. Foods to avoid for hyperthyroidism include iodine-rich items like seaweed, kelp, and iodised salt, as well as caffeine, highly processed foods, and gluten for autoimmune-related thyroid conditions.
Q. What is the nursing diagnosis for a patient with hyperthyroidism?
A. A nursing diagnosis of hyperthyroidism includes imbalanced nutrition, disturbed sleep, activity intolerance, anxiety, risk of cardiac complications, and altered body image due to weight and appearance changes.
Q. What are the key nursing interventions for hyperthyroidism management?
A. Key nursing interventions for hyperthyroidism management include monitoring vital signs, providing a calm environment, encouraging small meals, teaching relaxation, and educating patients on medication compliance and lifestyle adjustments.
Q. How is a nursing care plan for hyperthyroidism prepared?
A. A hyperthyroidism nursing care plan is prepared by assessing symptoms, setting goals like stabilising vital signs, promoting rest, ensuring nutrition, and creating interventions tailored to patient-specific needs.
Q. When should I visit a hyperthyroidism specialist or endocrinologist?
A. You should visit a hyperthyroidism specialist if experiencing unexplained weight loss, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, sweating, or eye changes. Early consultation ensures timely treatment and avoids long-term complications.
Q. Can you show hyperthyroidism pictures or images to recognise symptoms?
A. Yes, hyperthyroidism pictures and images can highlight symptoms such as bulging eyes, enlarged thyroid, or visible weight loss. However, diagnosis should always be confirmed by medical professionals.

10 Signs of Hypothyroidism That You Should Be Worried Of

7 Myths About Thyroid - This Is What You Should Know

What is Hypothyroidism? Understanding Underactive Thyroid and Its Impact on Health


